
Drake Hampton
Mar 23, 2022 15:42
A forex trading strategy is a mathematical formula used by a forex trader to determine when to purchase or sell a currency pair. Traders can employ a variety of forex tactics, including technical analysis and fundamental analysis. A competent forex trading strategy enables a trader to do market analysis and confidently execute deals while employing effective risk management approaches.
Forex strategies may be classified according to a specific organizational structure that enables traders to quickly identify the most appropriate approach. The figure below explains how each forex strategy fits into the larger framework and how the forex strategies relate to one another.

Forex trading needs you to consider a variety of aspects in order to develop a trading strategy that works for you. There are several tactics that may be used; nonetheless, it is critical to comprehend and be comfortable with the strategy. Each trader has individual objectives and resources, which must be considered while determining the most appropriate approach.
Three criteria can be used by traders to evaluate the appropriateness of various strategies:
Required time resource
The frequency with which trade opportunities arise
Typical range to the target
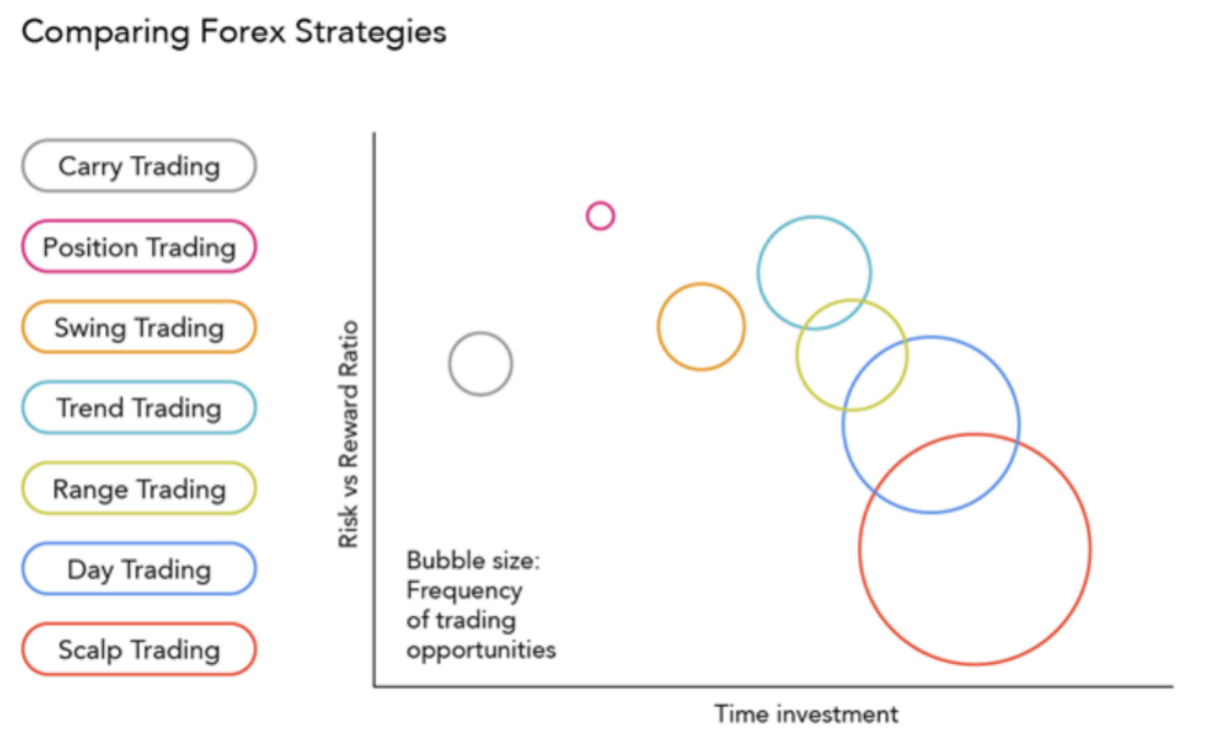
To make comparisons between forex strategies based on these three criteria simple, we've created a bubble chart. The vertical axis represents the 'Risk-Gain Ratio,' with the strategies near the top of the graph offering a greater reward for the risk incurred on each transaction. Typically, position trading is the approach with the best risk-reward ratio. The horizontal axis shows time investment, which is the amount of time necessary to actively monitor the deals. Scalping is the method that requires the most of your time resources owing to the high frequency with which transactions are executed on a frequent basis.
Price action trading is the process of analyzing previous prices in order to develop technical trading methods. Price action can be employed independently of an indicator or in conjunction with one. Although fundamentals are seldom employed, it is relatively uncommon for economic developments to be incorporated as a substantiating component. There are various other tactics that come into the price action category discussed previously.
Price action trading may be used to a variety of time frames (long, medium and short-term). Price action trading is highly regarded by many traders due to the flexibility to analyze using numerous time frames.
Numerous approaches exist for determining the support/resistance levels that are commonly utilized as entry/exit points:
Retracement of the Fibonacci sequence
Utilization of candle wicks Identification of trends Indicators
Oscillators
There are several types of price action trading: range, trend, day, scalping, swing, and position trading. These methods comply to a variety of distinct trading requirements, which are detailed below. The examples demonstrate a number of trading tactics for various strategies, as well as a selection of customizable alternatives for traders to pick from.
Range trading is finding major support and resistance levels and trading around them. This method is most effective in markets with little volatility and no obvious trend. This method is mostly based on technical analysis.
There is no fixed duration for each transaction because range bound methods may be used on any time frame. Risk management is a key aspect of this strategy, as breakouts are possible. As a result, a range trader wishes to close any open range-bound trades.
Oscillators are frequently employed as timing devices. Among the more common oscillators are the Relative Strength Index (RSI), the Commodity Channel Index (CCI), and stochastics. Price action is occasionally used in conjunction with oscillators to confirm range bound or breakout signals.
Numerous trading opportunity
Ratio of risk to return that is favorable
Requires substantial time investment
Requires a keen understanding of technical analysis
Trend trading is a straightforward forex technique that is employed by a large number of traders of all experience levels. Trend trading aims to maximize profits by capitalizing on a market's directional momentum.
Trend trading is often conducted over a medium to long time frame, as trends themselves vary in length. As with price movement, trend trading may include several time frame research.
Typically, an oscillator (RSI, CCI, etc.) serves as the entry point, while exit points are derived using a positive risk-reward ratio. Traders can either match or surpass stop level distances in order to preserve a good risk-reward ratio, e.g. If the stop loss level is 50 pips away, the take profit level should be at least 50 pips distant from the entry point.
Numerous trading opportunity
Ratio of risk to return that is favorable
Requires substantial time investment
Requires a keen understanding of technical analysis
While position trading is a long-term strategy that is primarily focused on fundamental factors, technical indicators such as Elliot Wave Theory can be used. Minor market swings are ignored in this technique since they have little impact on the wider market picture. This method is applicable to all markets, including stocks and FX.
As indicated previously, position trades have a longer time horizon (weeks, months, or even years!) and are thus designated for the more patient trader. Understanding how economic considerations influence markets, as well as detailed technical predispositions, is critical for projecting trading ideas.
Due to the full perspective of the market provided by longer time frame charts (weekly/monthly), key levels provide significant information for position traders. Technical analysis, like with the other methodologies, may be used to determine entry and exit positions.
Requires minimal time investment
Risk-to-reward ratio is really favorable.
There are really limited trading chances.
Requires an in-depth understanding of technical and fundamental analyses
Day trading is a method in which financial instruments are traded during the same trading day. That is, all positions are closed prior to the closure of the market. This might be a single transaction or a series of transactions throughout the day.
Trades can be very short-term (a matter of minutes) or very long-term (hours), as long as they are initiated and closed throughout the trading day.
Traders will attempt to enter positions when the price breaks over the 8-period exponential moving average (EMA) in the direction of the trend (blue circle) and exit with a risk-reward ratio of 1:1.
Numerous trading opportunity
Risk-to-reward ratio on a median basis
Requires substantial time investment
Requires a keen understanding of technical analysis
Scalping is a phrase that is frequently used in the forex market to refer to the technique of taking modest profits on a frequent basis. This is accomplished by repeatedly opening and closing positions throughout the day. This can be accomplished manually or via the use of an algorithm that follows predetermined parameters for when and where to enter and depart positions. The most liquid forex pairs are selected since spreads are often tighter, which fits the strategy's short-term nature.
Scalping is a trading strategy that focuses on short-term transactions with a low expected return, often on lower time frame charts (30 min – 1min).
As is the case with the majority of technical solutions, detecting the trend is the first step. Numerous scalpers confirm the pattern using indicators such as the moving average. Utilizing this trend's pivotal levels on lengthier time frames enables the trader to view the broader picture. These levels will result in the formation of support and resistance bands. Scalping inside this range can then be attempted utilizing oscillators such as the RSI on smaller time frames. Stops are put a few pips apart to avoid big fluctuations in the opposite direction of the trade. The MACD indicator is another valuable tool that traders may utilize to begin and exit deals.
Swing trading is a speculative approach in which traders seek to profit from range-bound and moving markets. Traders can enter long and short positions appropriately by identifying 'tops' and 'bottoms'.
Swing trades are considered medium-term investments since holdings are often held for a few hours to a few days. Longer-term trends are preferred because traders can profit from the trend at various stages along the way.
Similarly to the range bound method, oscillators and indicators may be utilized to determine the best entry/exit points and times. The main distinction is that swing trading is applicable to trending as well as range-bound markets.
Numerous trading opportunity
Risk-to-reward ratio on a median basis
Requires a keen understanding of technical analysis
Nonetheless, significant time commitment is required.
Carry trades entail borrowing one currency at a lower rate and investing it in a higher earning currency. This will eventually result in a transaction with a positive carry. This method is most frequently utilized in the foreign exchange market.
Carry trades are subject to interest rate variations between the connected currencies; hence, the duration of the trade benefits the medium to long-term (weeks, months and possibly years).
Carry trades perform best in strong moving markets, as the approach requires a longer time horizon. Prior to entering the trade, confirm the trend (higher highs and higher lows and vice versa). A carry trade involves two risks: currency rate risk and interest rate risk. As a result, the optimal time to open positions is at the commencement of a trend in order to fully capitalize on the exchange rate movement. Concerning the interest rate component, this will remain constant regardless of the trend, since the trader will continue to get the interest rate difference if the first listed currency has a higher interest rate than the second named currency, for example, AUD/JPY.
Could carry trading be beneficial to you? Consider the following pros and cons to determine whether this is a forex strategy that fits your trading style.
Time investment is minimal.
Risk-to-reward ratio on a median basis
This entails a significant appreciation of the FX market.
Trading possibilities are few.
This article discusses eight distinct types of forex strategies and illustrates them with real-world trading examples. When deciding on a trading strategy to follow, it might be beneficial to examine the amount of time necessary behind the monitor, the risk-reward ratio, and the frequency of trading possibilities. Each trading technique will appeal to a particular type of trader based on their own characteristics. By matching traders' trading personalities to the suitable approach, traders may finally take the first step in the correct way.

Mar 23, 2022 15:38

Mar 23, 2022 16:10